Our products rLDPE
General information on recycled low-density polyethylene
Low-density polyethylene (LDPE) is a thermoplastic from to the polyolefin family, and more specifically to the polyethylene family like high-density polyethylene (HDPE). It is one of the most widely used plastic materials in modern industry.
Recycled low-density polyethylene (rLDPE) could replace virgin LDPE in the plastic films of the future.
Some applications for recycled LDPE
Many different grades are available to meet all your process requirements.
rLDPE blown film extrusion grade
Blown film extrusion is a film-forming process. The vast majority of our available rLDPE are suitable for this process, enabling the formation of films and bags for a wide range of applications:
- Production of large bags, mainly for packaging various materials in the agricultural and chemical industries.
- Production of shrink films for palletizing or bundling (shrink-wrapping films).
- Production of small to medium-sized films, pouches and bags, such as shopping bags and trash bags.
- Production of agricultural films such as mulch films, tunnels and greenhouses.
- Production of waterproofing membranes and coatings for the construction industry.
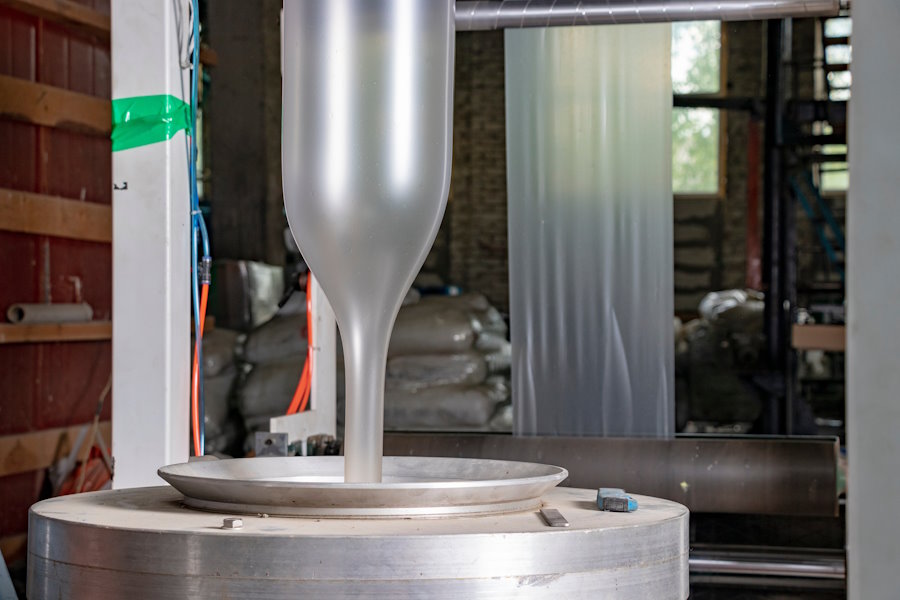


rLDPE pipe extrusion grade
Some of our rLDPE are available in extrusion grade for pipe and cable production. These rLDPE grades can be used for the production of water pipes, but also insulating cables or cable sheaths in the energy and telecommunications sectors.
Properties and characteristics of rLDPE
The ramifications of LDPE macromolecular chains give it great flexibility and resistance to impact, distinguishing it from HDPE.
LDPE can be either "radical" (R-LDPE or just LDPE) or "linear" (LLDPE). The first type takes its name from "radical" polymerization catalysts. Reactivity is very high, resulting in extensive and relatively anarchic branching. LLDPE synthesis involves the use of Ziegler-Natta or Phillips catalysts in the presence of comonomers: butylene (C4), hexene (C6) or octene (C8), which allows controlled branching sizes and thus a more "linear" LDPE.
LLDPE mainly have better elongation properties than rLDPE, making them preferable for stretch film applications.
When recycling films, it is extremely complex to separate these two types of LDPE, unless they are known and segregated at source. As a result, rLDPE is frequently a mixture of LLDPE and LDPE. Additives can also be found in rLDPE. For example, slip agents, which limit the adhesiveness of LDPE films and facilitate coil handling, antistatic agents such as glycerol monostearate (GMS) or calcite, which stiffens the material and increases its density, can be found.
When recycling films, it is extremely complex to separate these two types of LDPE, unless they are known and segregated at source. As a result, rLDPE is frequently a mixture of LLDPE and LDPE. Additives can also be found in rLDPE. For example, slip agents, which limit the adhesiveness of LDPE films and facilitate coil handling, antistatic agents such as glycerol monostearate (GMS) or calcite, which stiffens the material and increases its density, can be found.
Customer/supplier collaborative working methods and information about sources
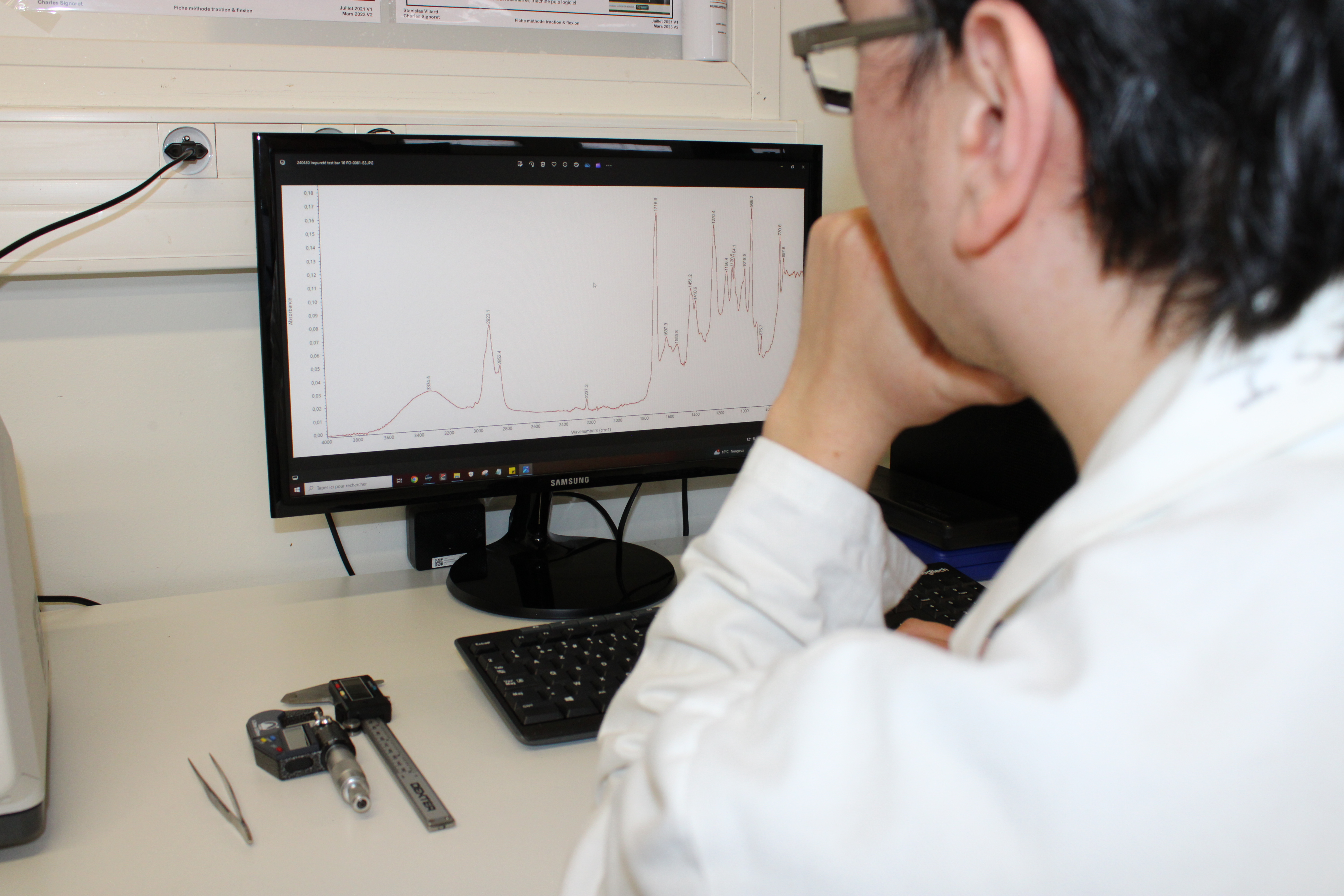
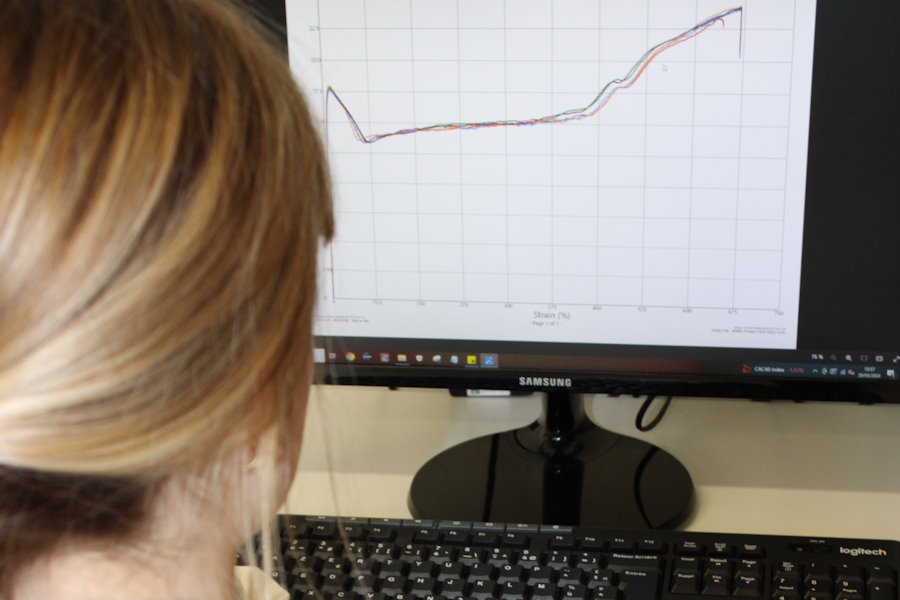
Customized characterizations to meet the challenges of each application.
Polytopoly's team of engineers works to propose solutions deemed best suited to the customer's constraints, backed up by its experience and track record in comparable applications.
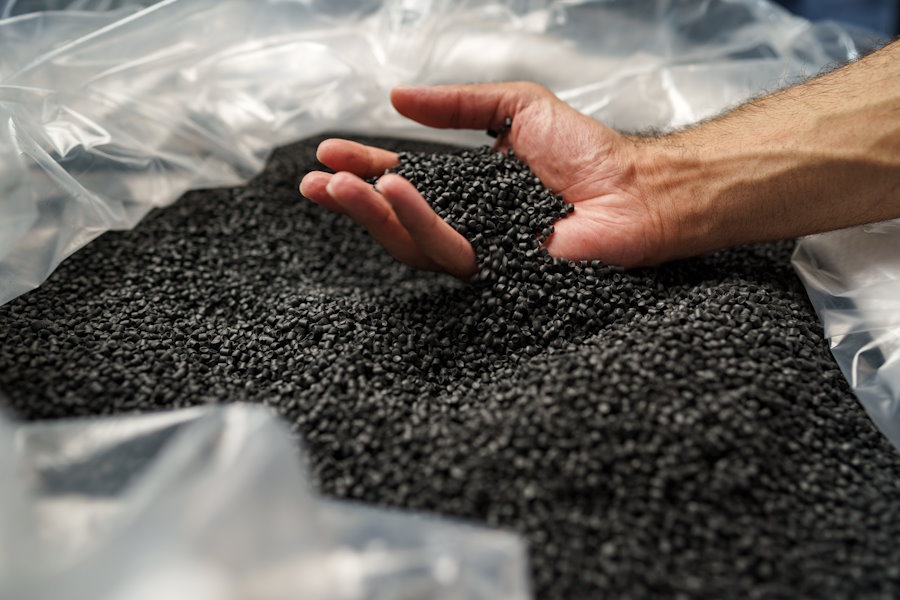

In order to assess the uses of its customers' products, Polytopoly offers reverse engineering, which gives a more detailed view of products that have already been approved.

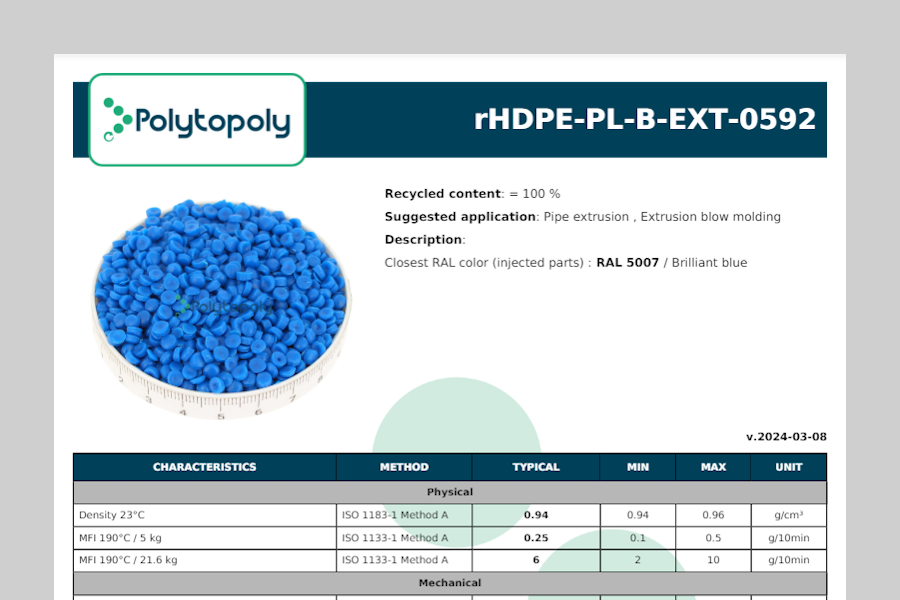
Product sources are diverse and identified for rigorous technical and regulatory traceability.